what is a pentose Biochemistry: pentose
Pentoses are a class of simple sugars that are crucial to the functioning of living organisms. These sugars have five carbon atoms, hence the name “pentose.” The most common pentoses found in nature are ribose and deoxyribose, which are the building blocks of RNA and DNA, respectively. In this post, we will explore the chemistry and biochemistry of pentoses, and their role in various biological processes. Pentoses are monosaccharides, which means they cannot be hydrolyzed into smaller sugars. They are aldehyde or ketone derivatives of pentanes, and have the molecular formula C5H10O5. The five carbon atoms in pentoses are numbered 1-5, with the carbon containing the aldehyde or ketone group typically designated as C1. The other four carbons are attached to hydroxyl (OH) groups, which give pentoses their characteristic chemical properties. One of the most important pentoses in biochemistry is ribose, which is a key component of RNA (ribonucleic acid). RNA is a nucleic acid that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where protein synthesis takes place. Ribose is also a component of several coenzymes, which are molecules that aid in catalysis of enzymatic reactions. For example, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) are coenzymes that play a crucial role in cellular respiration. Another important pentose is deoxyribose, which is a key component of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA is the genetic material that controls the development and function of all living organisms. Deoxyribose contains a hydrogen atom at the C2 position instead of an OH group, which distinguishes it from ribose. This modification makes DNA more stable than RNA and allows for the long-term storage of genetic information. Pentoses also play crucial roles in the metabolism of carbohydrates. They can be converted into other sugars, such as glucose and fructose, through a series of enzymatic reactions. Pentoses are also involved in the synthesis of various macromolecules, such as polysaccharides and glycoproteins. For example, the cell walls of many bacteria contain peptidoglycan, which is a polysaccharide composed of pentoses and amino acids. In conclusion, pentoses are a class of simple sugars with five carbon atoms that are crucial to the functioning of living organisms. Ribose and deoxyribose, the most common pentoses, are key components of RNA and DNA, respectively. Pentoses also play important roles in cellular metabolism and the synthesis of macromolecules. Understanding the chemistry and biochemistry of pentoses is essential for understanding the fundamental processes of life.
If you are looking for Pentose - Wikipedia you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pics about Pentose - Wikipedia like Pentose - Chemistry LibreTexts, Pentose - Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia and also Pentose - Chemistry LibreTexts. Here you go:
Pentose - Wikipedia
 en.wikipedia.orgpentose arabinose
en.wikipedia.orgpentose arabinose
Biochemistry: Pentose
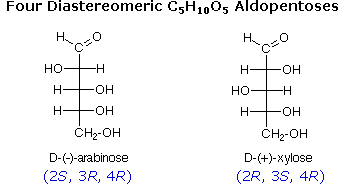 learnbiochemistry.blogspot.compentose pentoses
learnbiochemistry.blogspot.compentose pentoses
Pentose - Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
 alchetron.compentose
alchetron.compentose
Pentose - Chemistry LibreTexts
 chem.libretexts.orgpentose hexose triose libretexts also ochempal
chem.libretexts.orgpentose hexose triose libretexts also ochempal
Pentose - Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
 alchetron.compentose alchetron sugars
alchetron.compentose alchetron sugars
Biochemistry: pentose. Pentose alchetron sugars. Pentose arabinose